Executive Summary
Most providers participating in risk adjusted contracts view risk adjustment optimization as a function of revenue enhancement.
However, risk adjustment optimization is now an autonomous competency function critical for overall provider success in the risk adjustment sector. For a majority of risk participating providers with a significant patient demographic of federal lines of business; Medicare Advantage and Management Medicaid, risk adjustment factors, and HEDIS quality measures are the prime source for yielding short-term returns on investment.
This fiduciary value comes in either:
- 1) Increased reimbursement, from better quality scores eg; increased star rating or HCC additions.
- 2) Automating the process of chronic condition recognition, and, chronic condition case identification via prospective chart review.
This case study examines a two,100+ provider group based in Southern Nevada (referred to as “Provider Group Alpha”) with comprehensive clinical footprint covering primary care, specialty care, urgent care, surgical, hospice and hospital care. They have participated in risk-based contracts with the top five major payers, various regional Medicare Advantage ASOs, and Senior MA plans.
Provider Group Alpha’s Challenge
- Provider Group Alpha clinical informatics, CDI, quality, and provider relations functions are siloed business units. These units do not often communicate or find commonalities in their independent operational capability and technology investments preventing identification of enterprise solutions.
- CMO and CHAPS departments link risk adjustment optimization and quality improvement directly to provider performance incentives.
- Provider Group Alpha providers fear losing control over clinical data or risk missing a bonus payout due to a year of poor RAF performance and, therefore, resistant to enterprise solutions that change their clinical workflow.
- Sweeps hard deadlines and chart retrieval left a small window for the Clinical Review team to complete the work with enough time for RAPS submission
Vee Healthtek Solution
Building off the current prospective risk adjustment model, Provider Group Alpha targeted 11 common chronic conditions which could be validated by using analytics to extrapolate clinical indicators from Rx, DME, or ancillary documentation pertaining to uncaptured associated diagnoses
Linear modeling consisted of correlating a participating patient’s demographic profile, Rx/DME/Lab/Ancillary clinical indicators and computer model to authenticate suspected conditions (see Note 1*).
Using regression modeling, a correlational value is assigned to patients where ancillary documentation yields a high degree of certainty that a potential chronic condition diagnosis exists but not previously captured. If patient documentation shows a history of prescribed insulin but diabetes is not a captured HCC the chart is "flagged" within the EMR and sent to an offshore Clinical Reviewer for chart review and validation of the suspected condition. Once validated, a custom EMR script creates "flags" triggered by the offshore Clinical Reviewers to the primary care provider to assess and treat for the suspected condition validated by the data extrapolation and Clinical Reviewer.
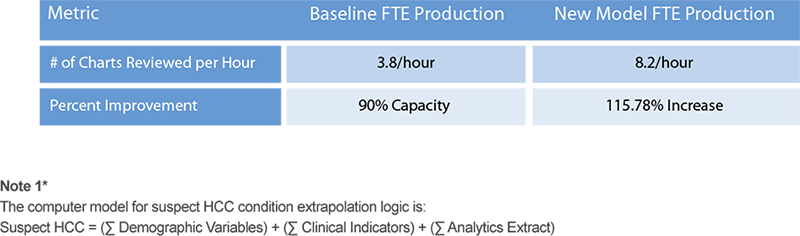
Under the new model, the Clinical Reviewers were able to meet the Sweeps submission deadlines, and the model was deployed directly from development to production without undergoing functional beta testing. The QA results exceeded 95% accuracy and yielded a 115.78% increase in Clinical Reviewer production.